Antibiotics do not treat viral infections and if
antibiotics are used too much, then the infections will build up an immunity.
Saturday, January 19, 2019
2) There is no evidence for evolution beyond the fossil record.
There is much more evidence for evolution than fossils
such as homologous structures and genetic code.
3) Structural Homologies only exist in animals, never in plants.
Plants too have homologous structures like those
seen in animals. In some plants like the pitcher, venus fly trap, poinsettia
and cactus, the leaves show different functions and shapes from the ‘normal’
leaves we think about. Each of these leaves is a homologous structure, derived
from a common ancestral form.
4) When the environment changes all species living in it will change to adapt to it.

Not all species in an environment will adapt to
a new environment and that is when natural selection occurs as some species
that haven’t adapted to the new environment will not survive.
5) Whales lost their hind limbs because they stopped using them.

As whales transitioned to an aquatic lifestyle,
their legs were of less use however, they did not completely lose their hind
limbs they are now just very small structures in the whale.
6) We have never been able to observe evolution.

We have observed evolution on a small scale in
plants who have evolved to resist pesticides and other similar situations.
7) We have never been able to observe speciation.
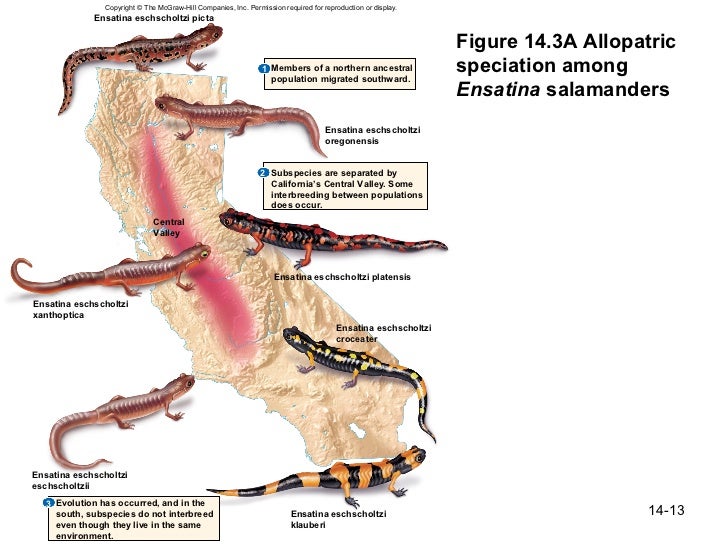
Speciation is defined as the splitting of one
species into two or more or the transformation of one species to another over
time. We have directly observed speciation in populations of Ensatina salamanders. All of the species
of salamander are proven to have come from one species.
8) Bird and bat wings can only be described as homologous structures, not as analogous structures.
Though bird and bat wings are homologous
structures, they serve the same purpose in their respective species therefore
they are analogous.
9) Evolution results in progress; organisms are always getting better through evolution.
One important mechanism of evolution, natural
selection, does result in the
evolution of improved abilities to survive and reproduce; however, this does
not mean that evolution is progressive. Natural selection does not produce
organisms perfectly suited to their environments. It often allows the survival
of individuals with a range of traits — individuals that are "good
enough" to survive. Hence, evolutionary change is not always necessary for
species to persist.
10) Individual organisms can evolve during a lifespan.

Evolutionary change is based on changes in the
genetic makeup of populations over time. Populations, not individual organisms,
evolve.
11) Natural selection involves organisms trying to adapt.

Natural
selection leads to the adaptation of species over time, but the process does
not involve effort, trying, or wanting. Natural selection naturally results
from genetic variation in a population and the fact that some of those variants
may be able to leave more offspring in the next generation than other variants.
12) Natural selection gives organisms what they need.
Natural selection has no intentions or senses;
it cannot sense what a species or an individual "needs." Natural
selection acts on the genetic variation in a population, and this genetic
variation is generated by random mutation.
13) Natural selection acts for the good of the species.
Natural selection has no foresight or intentions. In
general, natural selection simply selects among individuals in a population,
favoring traits that enable individuals to survive and reproduce, yielding more
copies of those individuals' genes in the next generation.
14) Natural selection always produces the best solution to a selective advantage.
Natural selection produces good enough solutions
but not always the best.
15) The fittest organisms in a population are those that are strongest, healthiest, fastest, and/or largest.
Though "survival of
the fittest" is the catchphrase of natural selection, "survival of
the fit enough" is more accurate. In most populations, organisms with many
different genetic variations survive, reproduce, and leave offspring carrying
their genes in the next generation.
16) Sexual selection does not support the idea of survival of the fittest.
Sexual selection does support the idea of survival
of the fittest because if two organisms that have the best genes have offspring
then those offspring would have the best genes.
17) There is no evolutionary advantage for a peacock having a large, fancy tail.

A peacock’s large and fancy tail is used to
attract females so that the males can reproduce. Therefore, it is an
evolutionary advantage.
18) Sexual selection only involves male competition.
Sexual selection involves male competition and
female choice of fitness.
19) Survival is the most important part of natural selection.
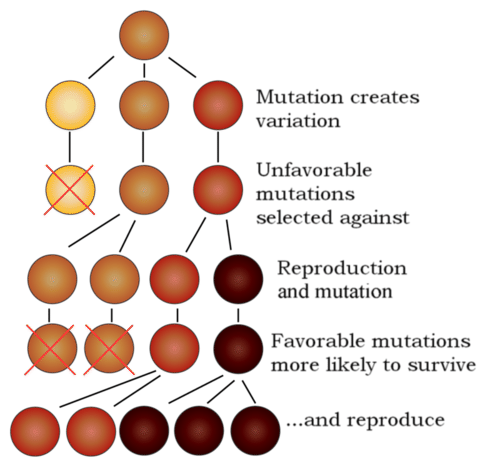
Survival is not the most important part of
natural selection because being the “fittest” organism and being the “fittest”
means that the organism reproduces to pass along its genes.
20) Organisms undergo mutations when they need to.
Organisms do not undergo mutations when they
need to because mutations are random and many organisms do not mutate even
though they might need to.
21) Evolution only affects physical traits and not behavioral traits.
Evolution can affect behavioral traits such as
mating calls in animals and turtles knowing to walk towards the moon when born. These are traits that assist organisms in survival and reproduction.
22) Evolution is “just” a theory.

Evolution has significant evidence in the form
of fossils, homologous structures, genetic code, and direct observation.
23) Only organisms (cells and larger) can evolve. Molecules cannot evolve.
Molecular
evolution does exist and is the process of change in the sequence composition
of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations.
24) Abiogenesis is a theory.

Abiogenesis has been proven to exist through
experiments by Oparin and Haldane and Miller and Urey.
25) The primitive atmosphere had to contain oxygen before life could evolve.

The primitive atmosphere
did not need to contain oxygen, it only required small organic molecules such
as carbon and hydrogen, among other more complex things.
26) The strongest evidence supporting the endosymbiotic theory is that mitochondria and bacteria are the same size and have a similar shape.
The stronger evidence of the endosymbiotic
theory is the presence of two membranes in membrane bound organelles.
27) Prokaryotic cells are less fit for their environment than eukaryotic cells
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/shigella-bacteria--illustration-758308491-5a02252f9e9427003c1759be.jpg)
Though prokaryotes are smaller and less complex,
they still have the ability to change and adapt to their environments.
30) The human eye was too complex to evolve.

The human eye was not always as complex as it
currently is, it evolved from an eye spot to its current structure.
31) It is uncommon for a trait to evolve independently in different lineages of organisms.

A trait evolving independently in different
lineages of organisms is known as convergent evolution.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)



